5 4: Liquidity Ratios Business LibreTexts
Full Cycle Accounting Advertising Examples: 50 Ideas to Grow Your CPA Firm
January 13, 2021
A higher cash ratio indicates a greater ability to pay off short-term obligations without needing to liquidate other assets, wait for customers to pay their invoices, or take on new loans. However, holding excessive cash can also mean a company is not maximizing its investment opportunities. At Deskera, we use an interactive tool to determine the financial strength of a company and the ability to generate cash internally through the liquidity ratios. A high current ratio means that a company has enough liquid assets to cover its immediate needs. A low current ratio indicates that a company may have difficulty paying its upcoming bills and seek additional financing to continue operations.
Understanding Liquidity Ratios
Investors favor stocks with robust liquidity ratios, signaling financial durability even in downturns. Shares with poor liquidity often suffer valuation discounts due to concerns over inflexibility and constraints on cash deployment needed to lift revenues, profits, and returns. The cash ratio is even narrower and only includes the absolute most liquid funds. The company could still service 88% of its liabilities, but would have to liquidate part of its inventories or wait for a longer period of time until income from accounts receivable arrives.
What is your risk tolerance?
Apple had $63.9 billion of funds available in total for the immediate payment of short-term debt. Between accounts payable and other current liabilities, Apple was responsible for roughly $123.5 billion when does the new york state tax department acknowledge e of short-term debt. The company has the same amount of current liabilities as it does cash and cash equivalents to pay off those debts if the result is equal to one when calculating the ratio.
Liquidity Management in Business
Inventory is, however, more liquid than land or buildings because, under most circumstances, it is easier and quicker for a business to find someone to purchase its goods than it is to find a buyer for land or buildings. A high cash ratio may indicate that management cannot utilize the business’s cash and struggles to find investment and growth opportunities. And a cash ratio below 1 is not necessarily bad news—especially if the firm has short credit terms with clients, efficient inventory management, and a short net trade cycle.
What is Liquidity Coverage Ratio?
Furthermore, a lack of liquidity means the company needs to cease vital functions like R&D, marketing, or growth initiatives in order to cover basic operating expenses. A positive ratio indicates the company pays its short-term obligations after liquidating current assets. A negative ratio means current liabilities exceed current assets and indicates financial distress.
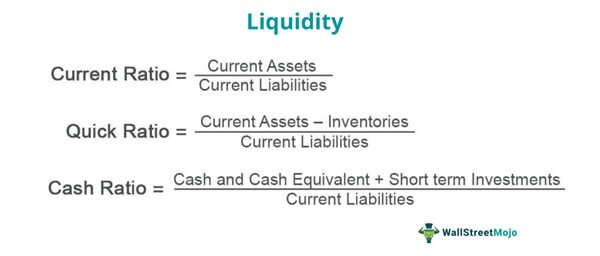
Net working capital (NWC) is equivalent to current operating assets (i.e. excluding cash & equivalents) less current operating liabilities (i.e. excluding debt and debt-like instruments). Of the ratios listed thus far, the cash ratio is the most conservative measure of liquidity. With that said, liquidity ratios can come in various forms, but the most common are as follows. Therefore, assets that can be sold and turned into cash in a short amount of time are considered to be highly liquid (and vice versa for assets with low liquidity). This is because the company can pledge some assets if it is required to raise cash to tide over the liquidity squeeze.
The business model also influences suitable liquidity and solvency levels for a brokerage. This means the company has earnings 5 times greater than its interest obligations. However, an extremely high ratio, like 10 or 20, could mean the company has too little leverage and is not optimizing assets.
- These ratios measure a company’s ability to meet its short-term obligations and give investors an idea of its short-term financial health.
- For investors, an unhealthy liquidity ratio below 1.0 is a sign of substantial risk.
- Liquidity ratios are simple yet powerful financial metrics that provide insight into a company’s ability to meet its short-term obligations promptly.
- Apple’s operating structure shows the company leverages debt, takes advantage of favorable credit terms, and prioritizes cash for company growth.
- This may overstate a company in a single good month or understate a company during the offseason.
Capital City Training Ltd is a leading provider of financial courses and management development training programmes, servicing the banking, asset management, and broader financial services and accounting industries. It is the result of subtracting the Current Liabilities from the Current Assets. Net Working Capital is often discussed when discussing the Current Ratio and our next liquidity ratio, the Acid-test Ratio, but it is not as popular as the two ratios. Recall that accountants use the term current to mean any assets or debts that are due within one year.
